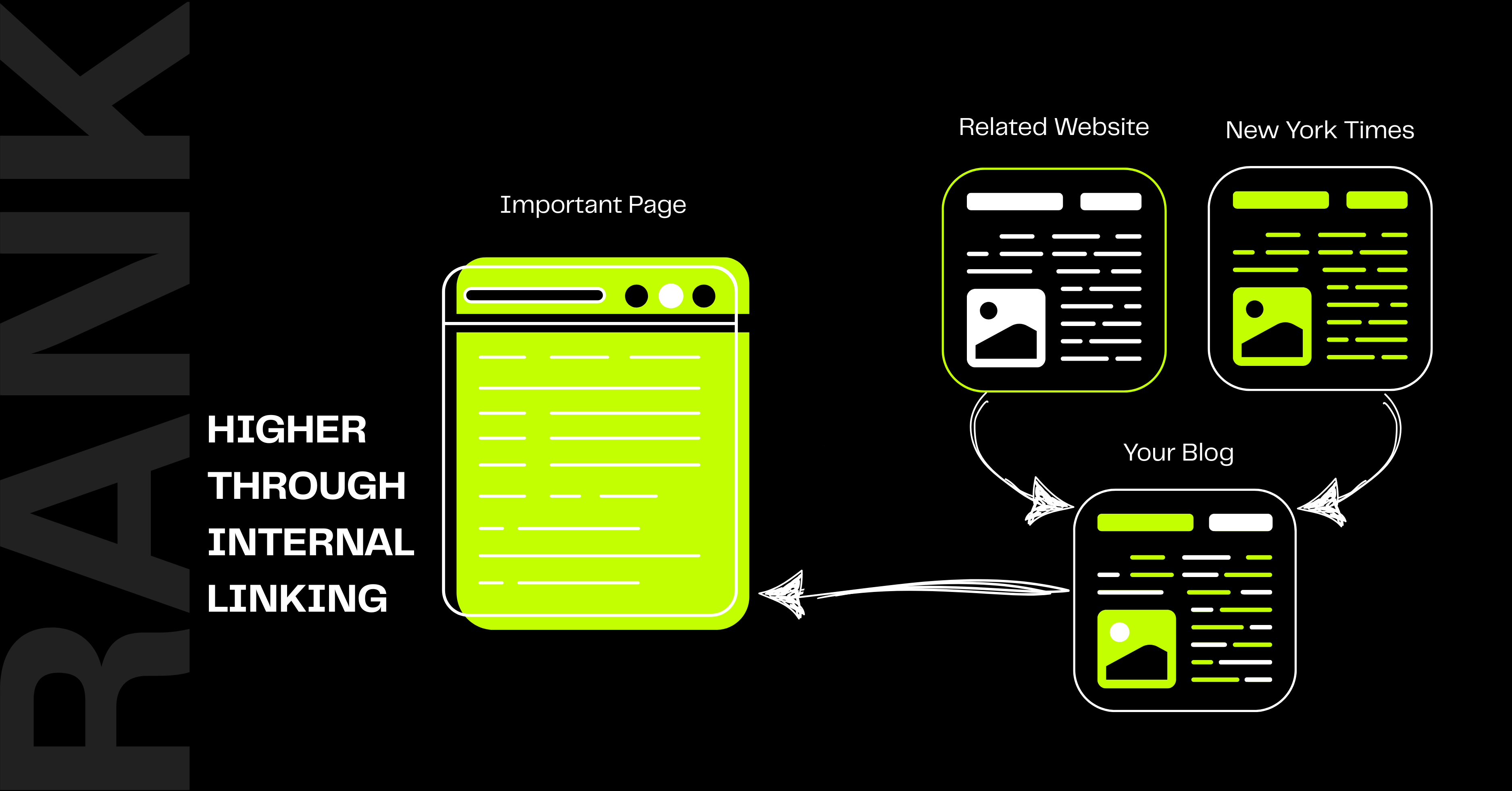
What Are Internal Links?
Imagine entering a huge library looking for a specific book, only to find all the books scattered around without any organization or indexing! It’s hard to find what you need, isn’t it? This is especially true when a website lacks a strong internal linking structure.
Internal links aren’t just a way to navigate your site’s pages; they’re a crucial tool for improving user experience and boosting your site’s search engine rankings. When used wisely, they help search engines understand your site’s structure and effectively distribute link equity, increasing the chances of important content appearing in search results.
In this article, we’ll explore how internal links can improve SEO, best practices for using them effectively, and why they can be the hidden factor behind your site’s ranking in search results. Read on to discover how to transform your site into an interconnected network that boosts its performance and attracts more visitors!
What is an internal link?
Internal linking is the process of linking one page on a website to another on the same site. By clicking these links, users are directed to other pages and sections related to your site. These links also help search engine robots, such as Google, discover new pages and understand the relationships between them more quickly.
All links placed in the site’s main menu, sidebar, page content, illustrations, footer, and other page elements influence the user’s understanding of the relationship between pages and determine their navigation path. All of these links are considered internal links and play an important role in improving the user experience and in search engines’ understanding of the site structure.
Internal links help improve a website’s internal search engine optimization through the following two main uses:
- Redirect the user to other pages of the website
- Help search bots find new pages
What are internal links in HTML?
Internal links in HTML are links between different pages within the same website, helping improve navigation and enhancing the user experience. These links are created using the <a> tag with the link address specified within the href attribute, which includes the address of the target page rather than an external site address. For example, an internal link could look like this:
<a href="about.html"> About Us </a>Internal links also help with search engine optimization (SEO) by distributing page power (Link Juice) and enhancing site structure, making it easier for search engines to understand the relationship between pages and index them more efficiently.
The difference between internal and external links
An external link is a link that connects pages on two different websites. Understanding this concept makes it easier to distinguish between internal and external links. Internal links connect pages within the same domain, while external links are primarily developed to cite or provide additional resources on other sites.
External links themselves fall into two categories:
- Inbound Links: Also known as backlinks, these are links created by other sites to your site.
- Outbound Links: Create links to pages on other websites.
With these comprehensive explanations, you’ll be able to clearly and precisely understand the precise meanings of the four key terms: internal links, external links, inbound links, and outbound links. To facilitate understanding and effective application of these concepts, here’s an organized table that summarizes these terms in a simple, easy-to-follow format:
| The term | Definition | Main objective | Impact on SEO | Practical example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Internal Links | These are links that connect pages of the same site. | Improve user experience, organize content, and direct search engines to index important pages. | Improves site structure, boosts internal page ranking, reduces bounce rate. | A link from an article about “SEO” on your site to another article about “internal links”. |
| External Links | These are links that go from your site to other sites. | Providing reliable sources to readers, improving the credibility of content, and strengthening relationships with other sites. | It may have a positive impact if directed to reliable sources, but too much of it may weaken the site. | A link in your article about “SEO strategies” leads to an article on a trusted site like Moz or Google Search Central. |
| Inbound Links – Backlinks | These are links that come from other sites to your site. | Increase domain authority, improve your site’s search engine ranking, and attract new visitors. | One of the most important factors in improving SEO is that the higher the quality of the links from trusted sites, the greater the positive impact. | A popular tech site links to your article on “Best SEO Strategies” in one of their blog posts. |
| Outbound Links | These are links that go from your site pages to external pages (like external links but in a broader sense). | Direct users to additional relevant content, enhancing the credibility of the information. | It may contribute to improving the user experience, but it must be for trusted sites so that it does not have a negative impact. | Link to a reliable research source when explaining a particular concept within your article. |
Why are internal links important on a website?
The definition of internal links is straightforward, but planning and developing a strategy for building these links, a process known as “internal linking” in SEO parlance, is not easy and must be done in accordance with the site’s SEO guidelines. Creating links between website pages is intended to facilitate navigation between different sites for search engine crawlers and visitors.
As a result, the importance of proper internal linking between website pages can be evaluated from two perspectives:
- From a search engine perspective and helping to improve SEO
- From a user perspective and helping to improve the user experience
Let’s see what impact internal linking has on improving the above and why sites that take internal linking seriously rank better on the results page.
Internal linking helps improve user experience
Including internal links on your website allows visitors to easily navigate between pages. The following sections will explain how this can enhance website navigation, reinforce vital material, and ultimately help you better understand concepts.
Ease of navigation on the website
Internal links on a website form a network of related and interconnected web pages. These links allow visitors to easily discover similar pages without having to return to the website’s main navigation. This improves the website’s user experience (UX).
Suppose a visitor lands on a web page about “Different Types of Search Engine Optimization.” If you provide links to similar materials on this page, such as on-page SEO, technical SEO, and off-page SEO, while discussing each type of SEO, the user is more likely to return to these sites for additional information.
Promote important website pages and content
Proper and original internal linking allows you to market your landing pages and other important website content to a larger audience. For example, on WasamWeb, all content related to digital marketing includes a link to the article “What is Digital Marketing?”, the site’s main article on the topic.
Gain a deeper user understanding of concepts
Internal links are powerful tools for webmasters and content writers to explain unfamiliar concepts, provide more information on an issue, or offer additional resources. Such information is more comprehensive and authoritative, increasing user engagement with website pages and building trust. For example, in this article, whenever we use a relevant, specialized word or phrase, we add an internal link to it so you can read more about it.
The importance of links in search engine optimization
Internal links directly impact a website’s SEO by helping search engines. In the list below, we’ve examined two reasons why:
- Better understanding of website structure by search engines
- Transferring the value and authority of web pages through links
Next, we’ll examine how internal linking helps improve SEO.
Better understanding of website structure through search bots
When you link between pages A and B on your website, you’re telling Google that the topics on these sites are related. Google uses this data to better understand the topics of the pages and how the different pages on your website are conceptually related.
Internal links between sites also help search engines in another way: identifying and indexing new pages. In general, search engines have a specific behavior for discovering new pages:
- First, you enter pages that have already been crawled and indexed.
- Then follow the links within these pages to get to the new pages.
If you don’t include links to new pages on previous sites, how will Google know they exist? Understanding the relationship between featured pages and new page discovery allows search engines to better understand your website structure, leading to higher rankings for these pages in the SERP.
Transfer of authority between web pages
When you build an internal link between two websites, some of the authority, or “PageRank,” is transferred from the more authoritative page to the less authoritative page. PageRank is one of Google’s algorithms that determines the value of websites. Transferring “link juice” is a term used in search engine optimization.
Let’s say webpage A has a high PageRank and many backlinks from other websites. When you add an internal link between this page and page B, some of the authority is transferred to page B. Identifying these high-authority pages on your website and leveraging internal linking allows you to transfer some of the website’s authority to lower-authority sites.
What are the types of internal links?
By now, you’ve learned the concept of internal link building and understood its importance in improving website SEO. Internal links are classified into two main types based on their location and use, as they work together to facilitate access to different pages and convey link value between them.
Types of internal links:
- Structural links: These are links found in the main menu, footer, or sidebar of various website pages. They play a key role in navigating between pages and conveying the value of the links.
- Contextual Links: These are internal links embedded within text content, primarily intended to direct users to related pages, enhancing the browsing experience.
Below, we will review each type of link in detail.
Structural Internal Links
If asked about the most important type of internal links, you can point to structural links, also known as navigational links, since they are mainly used to facilitate navigation within the site.
These links appear in different sections of the website’s home page, such as:
- Top Menu
- Sidebar
- Footer
- Breadcrumb Menu
These links are often repeated across all pages of the site, helping users navigate seamlessly between different sections.
The primary purpose of these links is to facilitate navigation between different pages, but they also play a pivotal role in transferring the value of links from home pages to internal pages, boosting their ranking in search engines.
For example, the top menu on the Wasam Web site contains different categories of site content, and appears on all pages of the site, allowing users to easily navigate between different topics and quickly return to the home page when needed.
It is important to note that all links in this list are internal links, but if the link contains a directive to an external site, it becomes an external link, such as clicking on the “Link Placers“ link that takes you to the official Link Placers website.
Based on their location within the page, structural links can be classified into several types, which we will discuss in detail in the following paragraphs.
Footer links
Footer links are the structural links that appear at the bottom of the page. These links take users to important sites such as the Contact Us page, About Us page, and FAQ page, which any visitor might need to quickly access.
Sidebar Links
Many websites include internal links in the sidebar on the right or left side of the page. Links in this area often direct users to popular and relevant pages and information. Many news websites or educational blogs use this feature to encourage users to visit additional, relevant pages on the website.
Internal Text Links
Internal links are embedded in the text and content of websites, and their primary function is to connect readers to pages containing similar material. These links are typically formed using descriptive words and phrases known as anchor text. An internal link in the text exposes related material to readers and tells search engines how to link to pages or blog posts.
Anchor text is the most important consideration when creating internal links between website pages, and it must be relevant to the content of the destination page. In the next section, we’ll show you how to build internal links and choose appropriate anchor text.
Internal link building strategy steps
So far, you’ve learned about internal linking and identified the different types of internal links. At this point, your question should be how and on what principles internal links are created. The principles for doing so are simply outlined in the list below.
- Using anchor text with keywords
- Create internal links from important pages to low-quality pages
- Use different anchor text to point to similar pages
- Analyzing internal linking status using Google Search Console
- Place internal links at the top of the page
- Pay attention to whether the internal link is Dofollow
- Using internal links to aid indexing
- Principles of internal linking from the home page
- Do not use internal linking tools
- Use internal linking to improve website structure
- Adding internal links to old pages
- Pay attention to the number of internal links
- Check the mobile version of the website
- Pay attention to the priority of the first link
Let’s see how you should use the above principles to build internal links.
Use keyword-rich anchor text
Anchor text, also known as anchor text, is the first and most important consideration when building links. In other words, you should optimize the use of keyword-rich anchor text in your internal links.
Anchor text is a key element when creating internal links, as it plays a vital role in directing users and search engines to the target page. When inserting an internal link, it’s essential to choose an appropriate word or phrase to represent the content the linked page points to, helping boost the page’s indexing and ranking in search results.
To improve your internal anchor text, Google recommends using various strategies such as:
- Exact Match Anchor Text: These are text that literally match the target keyword.
- Partial Match Anchor Texts: Contain the keyword combined with other words.
- Related Keywords: Where words and phrases related to the topic are used instead of the target term itself.
Examples of effective anchor text application:
- If you are writing an article about “Best SEO Strategies”, you can use the following text as an internal link:
- Learn the best SEO strategies to increase your website’s visibility on Google.
- You can improve your website by applying modern search engine optimization techniques.
- In the case of an article about “keyword analysis”, you can diversify the texts as follows:
- Find out how to choose the right keywords for your website.
- Learn the importance of keyword research in content strategies.
According to Google’s recommendations, overusing exact link text can make links look unnatural, so diversify your text and combine different types to improve user experience and boost your site’s SEO performance.
❝
Important note: When creating backlinks, avoid using texts that are exact 💡 matches to the keyword, as this may negatively impact your site’s ranking in search engines.
Create internal links from important pages to pages with low reputation
In previous sections, we discussed how creating an internal link from one page of your site to another transfers some of the authority from the source page to the destination page. This improves the destination page’s ranking in the results page. Consequently, one of the basic rules for using internal links is to direct them from more credible sources to less credible ones.
Let’s also point out that while these links may not have the same impact on rankings as gaining backlinks, they are not useless. This is why more experienced SEO professionals consistently build internal links from authoritative pages on their site to other sites. To achieve this, follow these steps:
Using various SEO tools, compile a list of the pages with the highest number of backlinks. For example, in the Links report in Google Search Console, the External Links tab, and the Top Linked Pages section, you can view a comprehensive list of unique backlinks to your website, as well as the number of backlinks received individually.
Pages in this list have higher authority because they have more backlinks, thus creating internal connections from them to pages with lower authority.
Use diverse anchor texts to point to pages with similar content
When creating internal links to pages related to similar topics, it’s important to diversify your anchor text rather than using the same text for each. Using the same anchor text to point to two different pages confuses both Google and users, which can negatively impact their understanding of the content and its ranking in search results.
Practical example of the effect of repeating anchor text
Suppose there are two articles:
- “What is digital marketing?” (Explains the concept and basics of digital marketing)
- “How to Become a Digital Marketing Expert?” (Discusses the skills and steps needed to become a professional in the field)
If you’re writing a new article about “The Benefits and Responsibilities of a Digital Marketing Expert” and want to include internal links to the two articles above, using the same anchor text for both pages, such as “Digital Marketing” or “Digital Marketing Expert”, could lead to confusion for search engines. In this case, Google might think both pages cover the same topic, when in reality, each article focuses on a different aspect of digital marketing.
The optimal solution for choosing internal link texts
Instead of repeating the same text, it’s better to use descriptive text that accurately reflects the actual content of each page. For example:
- “Definition of Digital Marketing and its Importance” (Refer to the first article)
- “Steps to Professional Digital Marketing” (Refer to the second article)
This diversity improves search engines’ understanding of the overall context of the content and helps users navigate between pages easily and clearly without confusion.
Analyzing the status of internal links using Google Search Console
Internal linking isn’t just about generating links; you need to periodically check your internal linking status. Google Search Console is the most effective tool for doing this.
To do this, go to the Links Report in the main Search Console dashboard and click on the Internal Links section.
This section contains information you can use to examine the status and structure of your site’s internal links. For example, an analysis might show that a site has thousands of internal links between its various pages, most of which are to “About Us,” “Contact Us,” “Privacy,” and other pages. This isn’t the best for SEO, but it may vary by site.
We recommend reviewing your internal links report in Search Console once or twice a year to address any low-quality pages with a high number of internal links.
Place internal links at the top of the page
Did you know that placing internal links at the beginning of an article can boost your site’s search rankings? SEO experts have shown that increasing the number of internal links on a page reduces bounce rates and increases dwell time. Simply put, when readers find internal links in the first paragraphs of content, they are more likely to click on them and explore other pages within the site, which leads to them spending more time interacting with the content.
Why should internal links be placed at the front?
To ensure a smooth user experience and maximize on-page SEO, it’s best to include internal links at the beginning of your article. In Wassam Web’s articles, we always include one or two internal links in the first paragraph, encouraging the reader to engage from the very beginning.
How does this affect your site’s ranking?
When a user spends more time on your page, Google sends positive signals that the content is useful and relevant to the search query, boosting its ranking in the search engine results page (SERP). So, don’t hesitate to include strategic internal links at the top of your page to ensure your site performs better and attracts more visitors!
Pay attention to the Dofollow feature in internal links
Dofollow is a link attribute that directs search engine robots to follow a link and pass its value to the linking page. As we mentioned earlier, the primary goal of creating internal links is to enhance page interconnectivity and convey link strength between pages, which improves a site’s search ranking. Therefore, when creating internal links on your site, make sure they include the Dofollow attribute in their HTML code.
Important Note: The nofollow attribute is typically used when creating links to external sites to prevent any value from being passed on to them. By adding this attribute to a link, you tell search engines not to endorse the content of the linked page and not to transfer link authority to it.
In some cases, plugins designed to add nofollow to external links may also apply the same nofollow to internal links due to incorrect settings or programming errors. Therefore, always review your internal linking settings and ensure they are working in line with your site’s SEO strategy.
Using internal links to help with indexing
Google typically discovers and indexes important website pages. However, this doesn’t apply to all websites, especially large sites with a large number of pages. In these cases, because the crawl budget is limited, Google may only index a certain percentage of the website’s pages.
This problem can be solved by creating internal links between pages. Creating internal links allows search engines to index deep and orphan pages on your website.
As a result, if you want certain pages on your website to be indexed and added to Google’s list, you’ll need to provide internal links to them in your navigation menu or link to them directly from other pages. Make sure to include these pages in your site map as well.
Internal linking from the home page
In most cases, the home page is the most important page on the entire site, as it typically receives the most backlinks and traffic. Therefore, it should be linked to the rest of the site’s pages strategically and systematically, so that some of its value is transferred to other pages.
For example, Hostinger added a link to its blog’s home page in the footer of its main site. This transfers some of the value and credibility from the homepage to the blog. The home page of the site links to all of its posts, and thus, this credit is gradually transferred to all blog content.
Another option is to add internal links to your main blog posts from your website’s home page.
Improve website structure
Internal linking can help you create a website design that allows Google and people to easily navigate to different pages on your site. In fact, internal linking is the core of your website’s structure.
The internal link links web page A to web page B, but pages A and B must also link to their own base category.
This is something e-commerce sites excel at. For example, in an online store, all pages containing the Women’s Watches product are linked together on the “Women’s Watches Category” page.
Adding internal links to old pages
One of the most effective techniques for boosting internal links is to include links in older pages and articles on your website. To do this, follow these steps:
- Find an old article on the site that is more than a year old.
- Make a list of articles published after the original article.
- Finally, include links to more recent, more relevant information about your site in different places throughout the previous article.
You can use this method for all old pages on your website.
Pay attention to the number of internal links
Internal links improve a website’s SEO, but if used excessively, they lose their effectiveness. According to Google, search engines can follow up to 100 links on a page. This number includes both internal and external links. As a result, it’s best to limit the number of links on each page to this range.
Of course, you can add more than 100 links to a website, but keep in mind that the more links you have, the less value and authority each one sends.
Review the mobile compatibility of the website
One question asked by SEO experts is whether there is a difference between the internal linking structure of a desktop and mobile website. Google’s response to this question is that the internal linking structure of the mobile and desktop versions doesn’t have to be identical, but the different versions of the website should be as comparable in terms of internal linking as possible.
Given the importance of this issue, it’s best to ensure that key internal links present in the desktop version are also included in the mobile version.
Pay attention to the priority of the first link
Often, you may have included internal links to another page twice on one of your website’s pages. This is typical when there are multiple links in your site’s navigation menu.
In such circumstances, the key issue is anchor text, as Google considers anchor text at the top of the page and simply reflects its value. That’s why anchor text for navigation links is so important.
Not only do these anchor texts create a large number of internal links in the navigation menu, they may also have a greater impact on the page than other anchor texts, so keep that in mind when building links.
Important internal linking strategy steps for your website
Here are the steps for developing an internal linking strategy, which will explain how to do it on a larger and more extensive scale. The steps required to do this are as follows:
- Identify the core pages of your website
- Create Content Clusters Using Internal Links
- Choosing the best anchor text
- Identify trusted pages for a website
- Improve the placement of new pages
Below is a breakdown of each of the steps mentioned above.
Determine the main pages of the website
The first step in an internal link building strategy is to identify the pillar pages on your website. Pillar pages are pages that are central to other pages and cover a broad topic. Identifying these pages helps you create cluster pages that cover subtopics in more detail. Cluster pages are supposed to be linked to the pillar pages via internal links.
- Pivotal pages should target broad keywords with high search volume.
- Homepages provide content for customers at the top of the marketing funnel, the stage where customers are curious about products and services and want general information about them.
For example, if the website content is in the field of advertising and marketing, then the topic of copywriting can be considered a central topic.
Create cluster pages using internal links
After identifying the main topics and creating the pivot pages, the next step is to expand the content by creating cluster pages. Each column of content should have subheadings that branch off from it, which helps better organize information and improve internal cohesion.
Organize content more precisely
To ensure cohesive cluster pages are created, spreadsheet programs such as Google Sheets or Excel can be used to organize the relationships between content. For example, if we have a central topic like “copywriting”, we could create the following cluster pages:
| Main topic | Cluster topics |
|---|---|
| Copywriting | What is copywriting? |
| Writing email ads | |
| Advertising writing courses | |
| Essential Tools for Copywriting | |
| Principles and basics of advertising writing | |
| Practical examples of copywriting |
Deeper levels of clustered pages can also be created within each branch. For example, “Email Copywriting” could be branched into:
- How to write an attractive email address
- Top Tips for Writing Call-to-Action (CTA) Button Text
The importance of internal linking between pages
Cluster pages should be linked to hub pages via internal links to ensure search engine optimization (SEO) and achieve the following benefits:
- Clarifying the objective relationship between pages for search engines
- Boost the authority of your hub pages and make them the most trusted source
Tools for organizing ideas and keywords
You can also use keyword research tools to get additional ideas and learn what terms users are searching for. Some of the most important tools include:
- Google’s automatic search suggestions
- The “Related Searches” section on the search results page
- Keyword Magic Tool
- Answer The Public Tool
Using this strategy, you can build a comprehensive content structure that helps improve your site’s search rankings and enhance user experience.
Choosing the best anchor text
So far, you’ve selected your main and cluster topics and written content for them. Now, you need to build internal links between these pages. The first step in the linking process is choosing the anchor text, which is the text that acts as a link. Since you have complete control over your internal link texts, you should optimize them as much as possible using SEO techniques.
SEO-optimized anchor text has three main characteristics:
- Concise and clear: Anchor text should be short to quickly explain the page’s topic to both users and search engines. Anchor text should ideally be between 1 and 5 words long.
- Related: Avoid using generic or vague anchor texts like “click here,” as they don’t properly communicate the topic of the page to search engines like Google.
- Optimized: As mentioned in previous sections, if you use keyword-aligned anchor text in a balanced manner, your site’s SEO won’t be negatively impacted. However, it’s best to use the keyword within the anchor text along with other words to avoid falling into the trap of over-optimizing.
Find recommended anchor texts in keyword research tools and add them to your spreadsheet:
| Main page topic | Suggested link text | Cluster Pages Topic | Suggested link text | Subtopics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Complete Guide to Copywriting for Beginners | – Ad Writing Guide<br>- Best Ad Writing Techniques<br>- Important Ad Writing Tips | Email Ad Writing: A Guide to Achieving Higher Conversion Rates | – Email Copywriting<br>- Improving Email Copywriting<br>- Copywriting Examples | – How to write email subject lines to increase open rates<br>- The difference between plain text and HTML emails |
| Best Copywriting Courses | – The best training courses in copywriting<br>- educational video on copywriting | The best courses to learn copywriting | – List of the best courses in copywriting to improve SEO<br>- Free Copywriting Courses That Are Worth Your Time | – The Best Courses to Learn Copywriting for SEO |
Identify trusted pages for a website
The most authoritative pages on a website have the largest number of backlinks. As we discussed at the beginning of this article, a backlink is a link created by other websites to your website.
Google uses backlinks as a positive indicator to assess a page’s authority and relevance to its topic, thus improving its ranking. So, if a page has a lot of backlinks, you can transfer some of its authority by linking to it from other pages. At this point, use SEO tools like Google Search Console and Backlink Analytics to identify the most authoritative pages on your website and compile a list of them.
Improve the placement of new pages
Internal linking is crucial if you haven’t published your website in a while and don’t have many backlinks. Start by creating new content or visiting pages that might benefit from performance optimization. Then look for opportunities to include internal links to other pages within the text of these pages.
After defining your content, use Google to identify relevant pages on your website. Let’s say we want to identify articles on Wisam Web that are relevant to the article “Technical SEO.” To do this, we enter a specific search phrase into Google.
As you continue searching, Google will show you a list of related pages in its index. To be more specific, you can copy links from the pages you select and paste them into your link building plan file. Then, create internal links that lead to more authoritative information.
Common Internal Link Building Mistakes and How to Fix Them
So far, you’ve learned the basic concepts of internal link building and how to develop an effective strategy to improve your website’s internal links. However, the process of building internal links doesn’t always go smoothly, and you may encounter various challenges during implementation. In this section, we’ll discuss some of the key challenges you may encounter while building internal links. Among the issues that require careful monitoring during the internal linking process between website pages are the following:
- Broken Internal Links
- Excessive Internal Links
- Do not use internal linking tools
- Orphan Pages on the site
We will discuss each of these issues separately in the following sections.
1. Broken Internal Links
A broken internal link is a link that directs the user to a web page that does not exist on the site. Broken internal links can occur for various reasons, the most important of which are:
- Deletion of the Destination Page
- Moving a Web Page to a New URL Without Updating the Link
- Typo in the Unique Link
How to find broken internal links
Broken internal links cause a poor user experience as users see a 404 error page when they click on them. This increases your site’s bounce rate, negatively impacting search engine optimization and inbound traffic. Your first question regarding these links will likely be how to detect them.
To detect broken internal links, use the methods listed below:
- Using the Scan Tool in Google Chrome
- Using Google Search Console
- Using Screaming Frog
- Using Google Analytics
Below is a breakdown of each.
Using the Scan Tool in Google Chrome
To use this tool, right-click on the web page and select Inspect. This will open the “Inspect” panel for you, and you should click on the “Console” tab. When you arrive at this tab, you’ll see a list of 404 page issues.
Using Google Search Console
You can also detect 404 errors on your website using Google Search Console. To do this, go to the Search Console dashboard, select the Index report, and select the Pages tab. This report contains a wealth of information about the indexing status of various pages on your website. The details section of the report displays all pages with 404 issues.
Using the Screaming Frog tool
Screaming Frog is a web-based tool that crawls various website pages and identifies broken links for you. After downloading and installing the software, enter the unique URL of the website into the tool and click Start. After completing the procedure, click “Response Code” on the next page, then “Client Error (4xx)” and filter. To access the source pages for broken internal links, click the “Links” tab at the bottom of the page.
Using Google Analytics
You can also detect pages with 404 errors using Google Analytics. To do this, log in to your Google Analytics account, then navigate from the Acquisition section to All Traffic. Next, select Channels, choose Organic Search from the menu provided, and save the list. Then, input the list into Screaming Frog for indexing. This method differs from the previous method in that Screaming Frog prioritizes pages based on the volume of traffic they receive.
Fix broken internal links
After identifying pages with 404 errors, you must fix them. There are three main ways to do this:
- Redirect the link: If a web page has moved to a different address, you can redirect the link to the new page. This ensures that users are directed to the correct page without negatively impacting your site’s search engine optimization (SEO).
- Update the Link: If there are spelling errors in the unique link (URL) or if the link is directing users to the wrong page, update the link to correct these errors.
- Remove the Link: In some cases, if the web page has been completely deleted and no longer exists, the best solution for broken links is to remove them from the site.
2. Large number of internal links (Excessive Internal Links)
One of the biggest mistakes you can make when building internal links is placing too many internal links on your website pages. This confuses site visitors and search engine bots, making it difficult for them to determine which links are important and actually relevant to the page’s topic.
Therefore, it’s better to focus on the quality of internal links rather than their quantity. Keep in mind that there’s no set rule that specifies the optimal number of internal links per page, but SEO experts recommend not exceeding 100 internal links per page. Additionally, you can use Google Analytics to identify internal links that haven’t received any clicks and remove them from the page.
3. Do not use internal linking tools.
There are many tools and plugins for internal linking, one of them is the Internal Link Juicer plugin for WordPress.
It’s best not to use internal linking tools for three reasons:
- Internal linking is difficult with tools: Internal linking components and tools cannot detect pages that require value or authority from other sites or pages on your website that are suitable for linking.
- Generating random link strings: Depending on the size of your website, each plugin can easily generate up to 1,000 internal links with relevant link strings. In previous sections, we mentioned that using too many matching link strings is considered spam by Google.
- Lack of user consideration: Internal links should be used not only to boost a website’s internal search engine optimization, but also to help people locate relevant material. Tools are unable to detect valuable internal connections for users.
4. The presence of orphan pages on the site
Orphan pages are pages that have not received any links from other sites on the site. In previous sections, we noted that Google search engines discover new sites through links on old pages. The lack of internal links makes it difficult or impossible for search engines to locate certain pages.
If Google can’t detect orphan pages, they won’t be indexed and won’t appear in the results page. The solution to this problem is to locate these pages on your site and build internal links from other pages. To locate these pages, use the following steps:
- Create a list of indexed pages for your website using Google Analytics.
- Discover Crawlable Pages with SEO Spider.
- Website SEO analysis and discovery of orphan pages.
We will explain each of the above points in detail in the following sections.
Create a list of indexed pages for your website using Google Analytics
Search engines have difficulty identifying orphan pages on your site, so compile a list of your existing pages (indexed pages) right away. This is easy to do using Google Analytics. In the main Analytics dashboard, go to the Behavior section in the sidebar:
Click on “Site Content” and set the report to “All Pages“:
Change your Google Analytics report from “few pageviews” to “many pageviews,” as orphan pages sometimes receive relatively few visitors. Then, select the Export button in the upper right corner of the screen to download the Analytics report file in your desired format.
Discover Crawlable Pages with SEO Spider
In the next step, you need to use SEO spider tools like Screaming Frog to discover crawlable pages on your website. This tool allows you to scan up to 500 unique links (URLs) for free.
Keep in mind that the SEO Spider tool doesn’t crawl pages that Google has already discovered and added to its index without any problems. This is the main benefit of this method. Save crawl data from the tool in the same format as your Google Analytics report.
Website SEO Analysis and Orphan Pages Discovery
In the next step, you’ll have two spreadsheet files: one containing the list of unique links (URLs) for your website, and the other containing the unique links crawled by Google. You’ll need to compare these two files together. Combining these two files should produce two columns like the following:
The first column is for crawlable URLs, while the second column is for all unique links. Ensure the formatting of all unique links is consistent across all rows, and use the MATCH function to perform an exact match between the unique links. The function will match the unique links to each other, displaying the unique links that are present in the Google Analytics report but not in the other column.
Orphan pages on your website that require internal connections are basically these additional unique links.
You should repeat the process of identifying orphan pages on your website regularly at various times. Although it takes a lot of time, this process helps your website gradually reduce the number of orphan pages until it reaches zero.
Frequently asked questions about learning to build internal links
After explaining the concept of internal links and how to use them correctly, we will review some frequently asked questions about this important SEO strategy:
How many internal links should I add per page?
There is no fixed number of internal links that works for every page. Rather than focusing on quantity, prioritize quality and relevance. Generally, longer content can naturally accommodate more internal links. A good rule of thumb is to include 3-5 relevant internal links for every 1,000 words of content, but this can vary based on your site structure and content type.
Should I use exact match anchor text for internal links?
While exact match anchor text is acceptable for internal linking (unlike external linking where over-optimization can trigger penalties), it’s best to use a natural mix of exact match, partial match, and contextual anchor texts. This creates a more natural linking profile and helps search engines better understand the context of your linked pages.
Do internal links pass PageRank like external links?
Yes, internal links do pass PageRank (or “link equity”) throughout your website, though typically with less weight than high-quality external backlinks. Pages with more internal links pointing to them generally receive more PageRank, which can help improve their visibility in search results.
How do I prioritize which pages to link to?
Focus on linking to:
- High-converting pages that drive business goals
- Important cornerstone content that covers topics comprehensively
- New content that needs visibility and ranking support
- Pages that are topically related to the source content
- Pages that need additional PageRank to compete in search results
Should I update old content with new internal links?
Absolutely. Regularly updating older content with links to newer, relevant content serves multiple purposes: it keeps older content fresh, helps search engines discover new content faster, and strengthens the overall internal linking structure of your website.
How do NoFollow attributes affect internal links?
In general, you should avoid using NoFollow attributes on internal links unless you have a specific reason (such as linking to login pages or other pages you don’t want indexed). Using NoFollow on internal links prevents PageRank from flowing to those pages, which can hinder their ability to rank.
Can internal linking help fix keyword cannibalization?
Yes, strategic internal linking can help address keyword cannibalization by establishing clear hierarchical relationships between similar pages. By linking from secondary pages to your main page on a topic (using relevant anchor text), you signal to search engines which page should be considered the primary authority on that subject.
Should I link to category/tag pages or only to specific content?
Both approaches have value. Linking to specific content pages provides direct value to users looking for related information. Linking to well-organized category or tag pages can help users discover multiple related resources and improves the navigational structure of your site. The key is ensuring that all linked pages provide value to the user.
How do I track the effectiveness of my internal linking strategy?
Monitor these metrics to evaluate your internal linking effectiveness:
- Changes in organic traffic to internally linked pages
- Improvements in average time on site and pages per session
- Reduction in bounce rates for linked pages
- Increases in crawl frequency (visible in Google Search Console)
- Improvements in rankings for target pages receiving internal links
Conclusion
Internal links are a key component of on-site search engine optimization (SEO), allowing pages to be strategically linked together. This approach facilitates user navigation and enhances search engine bots’ ability to understand the relationship between pages, which positively impacts a site’s ranking in search results.
Internal links can be classified into two main types: Structural links: found in the main menus, footer, and sidebar. Text links: Inserted within content to direct the user to related pages.
The most important rules for building effective internal links: Use relevant and moderately relevant anchor texts to match your keywords. Create internal links between home pages and deep pages to enhance site cohesion. Update old content and add new internal links to support new pages. Monitor the performance of internal links through Google Search Console to ensure there are no errors that hinder crawling and indexing.
Do you use an effective internal link building strategy? Share your thoughts or questions with us in the comments!